Difference between for loop and while loop in Python
Difference between for loop and while loop in python : In this tutorial we are going to explain the difference between the “for loop” and “while loop” in the python programming language. Loop is executed as a block of the codes number of times until a certain condition meets. The use of loop is common in the programming language like other languages. The flow of programming is written in the programming language and is used by sequential by the default value. We need to alter the flow of the program and the execution is due to specific code and needs to be repeated several times.
Below table shows the difference between for and the while loop:-
Basic of comparison |
for |
while |
format |
Initalization,condition checking, iteration statements which are written at top of the loop |
The initialization and condition checking is done at top of the loop. |
declaration |
for(initialization;condition;iteration) |
while (condition) |
Initialization |
In the loop initialization once done is not repeated |
In this loop initialization is done during condition checking then it is done each time when the loop iterates. |
use |
The “for” loop is used only |
The “while” loop is used only |
condition |
If the given condition is not put up in “for” loop then the loop will iterate infinite times. |
The condition is not put up in “while “loop it will provide the compilation error. |
Iteration |
This loop iteration statement is written on top and execute only after the statements in loop are executed |
In this while loop iteration statement can be written any time. |
The advantages of using loops:-
Following are the advantages of the loop in the python programming language,- By using the loop we don’t need to write the same code again and again.
- We can transverse over elements of the data structure as arrays or linked lists using loops.
Use of loop in python:-
The looping system will simplify the complex problems quickly.
Also used to alter the flow of the program instead of writing the same code again and again.
We can repeat code for the finite number of times.
The example as if we need to print the 5 numbers then instead of using print statement 5 times we can use the print inside loop which runs up to 5 iterations.
For loop in Python detail description
The “for loop” iterate over the sequence of items and the structure us different in python, c, c++, java. for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
We use the “in” keyword.
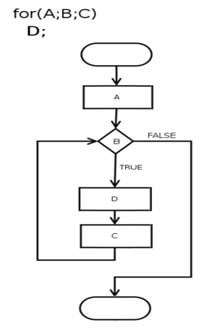
This loop is used to iterate the elements of the sequence and used when you have piece of code which you want to repeat at ‘n’ number of times.
The “for loop” has the two parts as header specifies iteration and body which is executed once as the iteration.
The header will declare the loop counter or loop and allow the body to know which iteration is executed.
This loop is used when a number of iterations are known before entering the loop.
Basically for loop comes from English word called for and used as the keyword in many languages.
The loop is used for the iteration over a set of statements which are repeated.
For loop is used for sequential of the transversal.
For Loop Syntax :-
for iterator_var in sequence:
statements(s)
Example:-
numbers= [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
sq=0
for val in numbers:
sq=val*val
print(sq)
Output:-
1
4
9
16
25
1) Range function:-
The function is used to loop through set of the code specified by the number of times and used this function.
It returns the sequence of numbers staring from the 0 by default and increments by 1 and will end by specified number.
Example:-
for x in range (6):
print (x)
Output:-
0
1
2
3
4
5
2) Using the else statement with for loops:-
We use combine else statement with the “for loop” and in while loop.
There is no condition in for loop which is based on execution terminates in else block which is executed immediately after block finish the execution.
Example:-
list= [“greeks”,”for”,”geeks”]
for index in range (len (list)):
print list [index]
else:
print”Inside Else Block”
Output:-
geeks
for
geeks
Inside else Block
3) Loop through a string:-
The strings are the iterable objects and contain the sequence of characters.
Example:-
for x in “Apple”
print(x)
Output:-
A
p
p
l
e
4) Break statement:-
The break statement used in body then it will stop executing and control shifts to first statement outside.
Example:-
fruits= [“Mango”,”Banana”,”Apple”]
for x in fruits
print(x)
if x==”Banana”:
break
Output:-
Mango
Banana
5) Pass statement:-
This statement we used to pass and write empty loops. Also used for the empty control statement, function and the classes.
Example:-
for x in[0,1,2]:
pass
Output:-
6) Nested for loop in python:-
The “for loop” used is present inside the “for loop” then called as the nested loop.
Example:-
for num1 in range (3):
for num2 in range (10, 14):
print(num1,””, num2)
Output:-
0, 10
0, 11
0, 12
0, 13
0, 10
0, 11
0, 12
0, 13
0, 10
0, 11
0, 12
0, 13
7) Continue statement:-
We can stop the current iteration of the loop and continue with the next iteration by using the continue statement.Example:-
fruits= [“Mango”,”Banana”,”Apple”]
for x in fruits
if x==”Banana”:
continue
print(x)
Output:-
Mango
Apple
8) A real-time example of for loop:-
The thing is repeated again and again then you can use the looping concept.The for loop is used if we want to do something at a specific number of times,
In kitchen, we are doing some item which requires 10 tomatoes chopped.
Then the process starts,
- Clean it
- Cut edges
- Swiss it
- Slice into small pieces with knife.
The same process will be applicable for the reaming 9 tomatoes.
In python language we can use the “for loop” to do a sequence of steps for the specific number of times.
Example:-
For tomatoes in range 10:
Clean it
Cut edges
Swiss it
Slice into small pieces using the knife
print(“chopped {} tomatoes”. format (tomatoes+1)
Detail While loop in Python 3 Description:-
This loop is used to repeat a block of code and Instead of running code once it will execute it multiple times until certain condition meets.
The loop used to iterate block of code repeatedly until the given condition returns false.
The difference between the while loop and for loop is that in while loop we are not certain of a number of times loop requires execution.
In for loop we need to run the loop when we use it.
hile loop in Python 3 Syntax:-
while condition:
#body of while
The body is a set of python statements that require repeated execution and the set of statements that executes repeatedly until the given condition returns false.
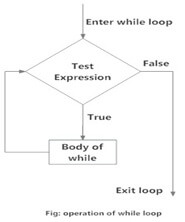
The while execution is as follows:-
Firstly given condition is checked and if the condition will return false the loop is terminated and control will jump to the next statement in the program after the loop.
The condition will return true the set of statements inside loop are executed and the control will jump to the beginning of loop for next iteration.
These two steps are repeated as long as the condition specified in while loop remains true.
Example:-
In this example of while loop we have num and display num value in loop and the loop has increment operation and increase the value of num.
The loop must have increment and the decrement operation else loop is runnel and cover the infinite while loop.
num=1
while num<10:
print(num)
num=num+3
Output:-
1
4
7
1) Infinite while loop:-
The example below print 1 indefinitely because from the inside loop we are not updating value of num and so the num will always remain 1 and condition num<5 return true.
Example:-
num=1
while num<5:
print(num)
Output:-
1
2) Nested while loop:-
The while loop which is present in the while loop is called the nested loop and the example below will explain the loop.
Example:-
i=1
j=5
While i<4;
while j<8:
print(i,””, j)
j=j+1
i=i+1
Output:-
1, 5
2, 6
3, 7
3) While loop with else block:-
The ‘else’ block is associated with while loop and the ‘else’ which is optional. It will execute after loop finishes the execution.
Example:-
num=10
while num>6:
print(num)
num=num-1
else:
print(“loop is finished”)
Output:-
10
9
8
7
Loop is finished
4) Continue statement in while loop:-
The program control will reach the continue statement and skips the statement after “continue”.
Then it will shift to next item in sequence and executes the code for it.
Example:-
i=0
while(i<8):
i+=1
if(i==6):continue
print (i)
Output:-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
5) Real-time example of while loop:-
You sitting on the coach want to receive the friend before he rings the bell.
You will do the following things,’
You open the door and check if he comes
No not
Then close the door again and continue watching TV.
Again you open door and check if he comes
If not then the close door and sits again
The process is repeated until the friend arrives.
If we want to implement the condition you can use the while loop and then,
Example:-
while(FriendNotArrived):
open the door
check if he has come
if friendArrive: Break
else:
close the door and continue watching TV
print(“Friend has not arrived yet”)
Performing the sequence of steps for specific time then you use the “for loop” if you want to do sequence of steps until condition is satisfied use the while loop.