Python Array using module and numpy library
Array using module and numpy library
In this tutorial we are going to discuss the python array module and the numpy library one by one. Python does not have built-in support for Arrays, but Python Lists can be ... An array is a special variable, which can hold more than one value at a time. Difference between the array and the list in python Is that list are flexible and hold arbitrary data of any type. The array can hold the data of same data type only.
Array using Array module:-
You can identify the location of any friends by knowing the count of step and so on.
Array is handled by module named “array” and the user can treat the lists as arrays.
The array is also called as the data structure and holds the fixed number of elements of the same data types.
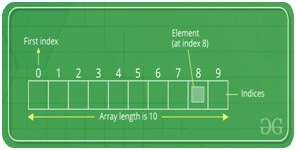
It consists of the element and the index. The index has the location where element is present.
All the elements have the indices band they start from 0.
Now python array is collection if the similar type of objects and will store the same items in the memory location.
The array idea is the storage of the multiple items in same type together.
The type is specified at object creation time and type code of single character.
The overall calculation becomes easier and multiple items are stored. The offset of base is also calculated.
If you crate array using the module all elements should be of the same type.
Difference between the array and the list in python Is that list are flexible and hold arbitrary data of any type. The array can hold the data of same data type only.
-
Importing a python array :-
If the python array is installed on your machine you can import it as below,
Import array
Creating a python array:-
To create a array by using the piece of code as,
Class array. Array (typecode[initialize])
Example of creating an array in python as,
Array=array (’a’ [9, 4, 5, 6])
Output:-
(‘a’ [9, 4, 5, 6])
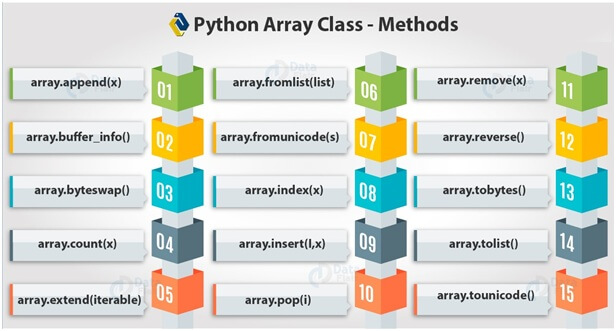
Some functions of the array module are as follows :-
The array module has the functions by using this we perform array operation as:-
- Create the array of specific element.
- Traverse an array element.
- Inserting the element into the array.
- Extracting the element from the array.
- Inserting the array.
- Deleting an element from the array.
The following are the most important functions in the array module:-
insert(i, x) |
Inserts an item x at the index i in the array. |
pop((i) |
Removes an item with the index i from the array and returns it. |
remove(x) |
Removes the first occurrence of an element x from array. |
reverse() |
Reverses the item of an array. |
count(x) |
Counts the number of occurrences of x in array. |
index(x) |
Returns the first occurrence of x in the array. |
append(x) |
Appends a new item to the end of an array |
extend(iterable) |
Appends items from iterable to the end of an array, items in iterable must be of the same type as array. |
Access the array elements in python:-
Use the indices for accessing the array elements.
The following example will show how to access the element,
Example:-
Import array as arr.
a=arr.array (‘a’, [2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
print (“First element:”,a[0])
print (“First element:”,a[2])
print (“First element:”,a[-3])
print (“First element:”,a[-6])
print (“First element:”,a[-4])
The index will start from 0 and not from the 1 as the lists.
Transversing through an array using for loop:-
The transverse of the element of array using the for loop and print the elements as shown below:-
Example:-
Create the array of int type:-
Array=array.array(‘a’,[1,2,3,4,4])
Transverse the array and print each using loop
For x in array
Print(x)
Output:-
1
2
3
4
4
Slicing of a python array:-
The access can be done by the slicing operator of python array.
The slicing of the python array is discussed from the following
Example:-
Import array as arr
Number_ list= [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
number_array=arr.array(‘a’.number_list)
print no from 3rd to 5th
print(numbers_array[2:5])
print no beginning to 4th
print(numbers_array[:-5])
print no 6th to end
print(numbers_array[5:])
print no beginning to end
print(numbers_array[:])
print no from 1st to 5th
print(numbers_array[1:5])
Output:-
array(‘a’[5,6,7])
array(‘a’[2,3,4])
array(‘a’[8,9])
array(‘a’[2,34,5,6,7,8,9])
array(‘a’[3,4,5,6,7])
Length of an Array:-
The use of len() method is to return the length of the array to check number of elements in the array.
Example:-
Return no of elements in array
bike1 = "shine"
bike2 = "royal enfield"
bike3= "splender"
X= [bike1, bike2.bike3]
x = len(bike)
Output:-
3
-
Inserting Array elements in python :-
You can use the append () method to add an element into the array.
Example:-
add element to bike array
bike.append(“splender+”)
print (bike)
Output:-
[‘shine’,’royal enfield’,’splender’,’splender+’]
This function removes the element at the position mentioned in its argument, and returns it.
Extending an array element:-
The array element contain the extend () function of the array, module and will append the items from list, tuple, set and array.
The items must be the same type array Example is given as follows:-
Example:-
Import array as arr
Create array of type int
First _array=arr.array (‘a’, [3, 2, 4, 5, 6])
Create another array of type int
Second _array=arr.array (‘a’, [1, 2, 4, 5, 6])
Print the Extended array
Print (‘extended first array with second array:’ first array)
Output:-
Extended first array with second array is:(‘a’,[3,2,4,5,6,1,2,3,4,5,6])
Python array methods :-
array.append(x):-
This will append the item x to array.
Example:-
arr.append (2)
array(‘a’,[3,4,5,6,6,7,7])
array.buffer_info():-
This will return that holds the address in memory and the length of elements in buffer that hold content in array.
array.buffer_info ()
array.byteswap():-
This will perform an operation of bytes wrap on an array.
Arr.byteswap ()
Arr
array. count(x):-
Let us find out the 2s in the python array.
arr=array. Array(‘i’,[1,2,7,2,8,3,2,2])
arr.count(2)
Output:-
4
array.fromlist(list):-
It will append the item from list to the python array.
array.fromlist([7,8])
arr
array(‘i’,[1,2,3,4,5,5,6,8,5,7,9])
array.index(x):-
The index will give the first occurrence in x in python of array.
arr=array. Array ('i',[1,1,2,4,3,5])
arr.index (3)
Output:-
2
array.insert(I,x):-
arr.insert(1,7)
arr
array (‘i’,[1,3,7,5,7,4,8])
It will insert element 3 at 1.
array.pop (i):-
This lets us drop the element at the position i.
arr.pop (4)
Output:-
4
array.remove(x):-
This will remove the first occurrence of an element from the python array.
arr
Array (‘i’, [1, 2, 4, 3, 5])
array.reverse():-
This operation will reverse the python array.
arr.reverse ()
arr
Array (‘i’, [5, 3, 4, 2, 1])
array.tobytes():-
It will return a representation in bytes of the value in python. This is same as array.tpstring().
arr.tobytes ()
- array.tolist():-
The array operation will convert into the list.
arr.tolist ()
[5, 3, 4, 2, 1]
- array.tounicode():-
This is the operation convert Unicode string and need Unicode array for this.
unicodearr.tounicode ()
‘Hello world’
Array using numpy library:-
The numpy is the high performance multidimensional array which is also called as general purpose array package.It is the fundamental set of packages for computing with the python and will contain the features are as follows,
- It has sophisticated functions.
- Have powerful n dimensional array objects.
- Is very useful algebra for Fourier transform and random number of capability.
Numpy can be also used as an efficient multidimensional container of generic data.
The arbitrary data can be defined by using the numpy which will allow seamlessly and speedily integrate the database.
Already we came to know the numpy arrays in python.
Numpy array is central data structure of its library.
This library full name is the “numeric python” or the “numerical python”.
Pythhon library called numpy is core library for the scientific computing of the python.
It will contain the tools and technique that can be solved on the computer mathematical models in engineering.
To work with the arrays high level mathematical function will operate on matriceof array.
The tool of high performance array object is a powerful data structure for computing the array and the matrices and the arrays.
The numpy is the open source library available in python in mathematical, data science programming.
The library is used to perform the mathematical and statistical operations.
Numpy tool is used for any scientific project in python.
It will work perfectly for the multidimensional arrays and matrix multiplication.
It will work with the n dimensional array, random number, Fourier transformation.
It deals with the programming language with multidimensional arrays and the matrices. It will also support mathematical operations and is essential function.
Basically numpy is memory efficient and it can handle large amount of data than any library. It is very convenient to use for matrix multiplication and reshaping.
Create an empty numpy array :-
You can initialize the empty array and make use of the initalial placeholder which can be filled up afterwards.You can also initialize the arrays with the ones and the zeros they can create arrays that can fill up the space value.
Creating the array of ones:-
np.ones((1,2))
Creating the array of zeros:-
np.zeros((1,3,4)),dtype=np.int12
Creating an array with the random values:-
np.random.random((1,3))
Creating the empty array:-
np.empty((1,2))
In the above example the np.ones, np.random.random (), np.empty, np.full () can be the only thing that you need to make array with ones and the zeros.
To create an array in Numpy is use of Python List
There are many ways to create the numpy array which will be converted as you read.
One of the most common ways is to create one from list or list like object by passing it to np.array function.
Create an array
Example:-
Import numpy as np
List1= [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
Arr1d=np.array(list1)
Output:-
Array [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
They can use the +,-, / or % to add, subtract, multiply, divide and calculate.
Shape of Array:-
You can check the shape with object shape by the name of the array.
Import numpy as np
a = np.array ([1, 2, 3])
Print (a.shape)
Print (a.dtype)
(3,)
int64
Mathematical operation in numpy array:-
Numpy is handy because it also has functions to do, the np.add(),np.subtract(),np.multiply,np.divide() and np.reminder().The exponent and square root arrays are used as np.exp () and np.sqrt (), sins or cosines of np.sin () and np.cos ().
The mathematical array operations are as follows:-
Numpy_array_from_list+10
Output:-
array([11,19,16,13])
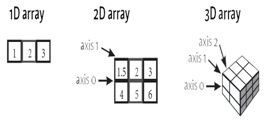
The two dimensional array has rows and the column rows are indicated as dimensional array and has rows and columns.
The number of axis will go with number of dimensions in the 3rd array.
How To Install Numpy :-
We will learn how to install the numpy as follows,- Start to install and make sure that you have properly installed it.
- If the python library already present then skip this section and go on.
Python installation:-
The numpy installation steps should be followed as:-
- Go to command prompt and type pip install numpy.
- After completion go to the IDE and then import it by numpy as np.
Single-dimensional Numpy Array:
Import numpy as np
A=np.array([1,2,3])
Print (a)
Output:–
[1 2 3]